World Book
Barbados
Introduction
Barbados, an island nation in the Caribbean, boasts a rich history that began with its settlement by the British in 1627. Initially uninhabited, the island quickly became a focal point for sugar production, although by 1720, it had lost its leading position in the industry to the Leeward Islands and Jamaica. The mid-20th century was a transformative period for Barbados, marked by significant social and political reforms that culminated in the island's independence from the United Kingdom in 1966. In a historic move in 2021, Barbados transitioned to a republic, further solidifying its sovereignty and national identity.
Neighboring countries
Saint Lucia - Saint Vincent and the Grenadines - Trinidad and Tobago
Geography
Area
Total: 430 sq km
Land: 430 sq km
Water: 0 sq km
Climate
The climate of Barbados is characterized as tropical, with a distinct rainy season occurring from June to October. This climate contributes to the island's lush landscapes and biodiversity, making it a unique destination in the Caribbean.
Natural resources
Barbados is endowed with several natural resources, including petroleum, fish, and natural gas. These resources play a crucial role in the island's economy and development strategies.
People and Society
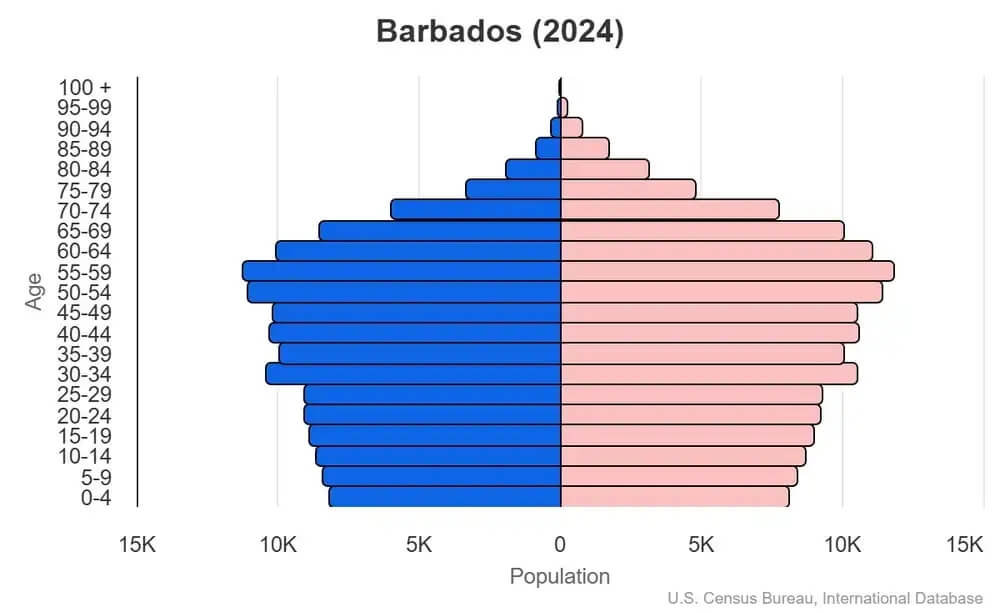
Population
Total: 304,139 (2024 estimated)
Ethnic groups
The population of Barbados is predominantly of African descent, comprising 92.4% of the total demographic. Other ethnic groups include mixed (3.1%), White (2.7%), East Indian (1.3%), and a small percentage of other groups (0.2%) and unspecified (0.3%) as of the 2010 estimate. This diverse ethnic composition reflects the island's complex history and cultural influences.
Languages
The official language of Barbados is English, which is used in formal settings, while Bajan, an English-based creole language, is widely spoken in informal contexts. This linguistic diversity enhances the cultural richness of the island.
Religions
The religious landscape of Barbados is predominantly Protestant, accounting for 66.4% of the population. This includes various denominations such as Anglican (23.9%), Pentecostal (19.5%), and Adventist (5.9%). Other religious affiliations include Roman Catholic (3.8%), other Christian denominations (5.4%), Rastafarian (1%), and those identifying with no religion (20.6%). This religious diversity contributes to the social fabric of the nation.
Population growth rate
The population growth rate is estimated at 0.23% for 2024, indicating a stable demographic trend in the country.
Government
Government type
Barbados operates as a parliamentary republic and is recognized as a Commonwealth realm, reflecting its historical ties to the United Kingdom.
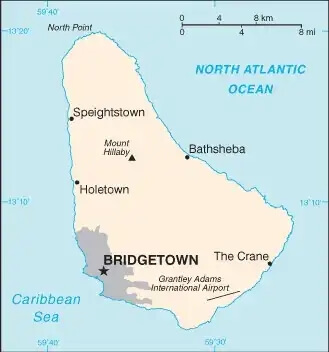
Capital
Name: Bridgetown
Executive branch
The chief of state is President Sandra MASON, who has been in office since 30 November 2021. The head of government is Prime Minister Mia MOTTLEY, serving since 25 May 2018, leading the country through various reforms and initiatives.
Diplomatic representation in the US
The chief of mission is Ambassador Victor Anthony FERNANDES, who has been serving since 18 September 2024.
Diplomatic representation from the US
The chief of mission from the US is currently vacant, with Chargé d'Affaires Karin B. SULLIVAN serving since January 2025. This position also includes accreditation to several other Caribbean nations, highlighting the strategic diplomatic relationships in the region.
Economy
Economic overview
Barbados is classified as a high-income economy within the Eastern Caribbean, characterized by a high standard of living compared to its regional peers. The economy is primarily driven by key sectors such as tourism, construction, and finance, which have been instrumental in recent GDP growth. However, the country faces challenges, including a declining yet substantial public debt, necessitating support from the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Additionally, Barbados is susceptible to natural disasters and relies heavily on import partners for various goods and services.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.634 billion (2024 estimated)
$5.428 billion (2023 estimated)
$5.214 billion (2022 estimated)
Real GDP per capita
$19,900 (2024 estimated)
$19,200 (2023 estimated)
$18,500 (2022 estimated)
Exports
$2.228 billion (2017 estimated)
$2.41 billion (2016 estimated)
$2.358 billion (2015 estimated)
Exports - partners
USA 22%, Jamaica 17%, Trinidad & Tobago 8%, Canada 6%, Guyana 6% (2023)
Exports - commodities
The main commodities exported include liquor, refined petroleum, packaged medicine, margarine, and baked goods (2023).
Imports
$2.12 billion (2021 estimated)
$2.213 billion (2017 estimated)
$2.238 billion (2016 estimated)
Imports - partners
The primary import partners are the USA (32%), Trinidad & Tobago (19%), Netherlands (6%), UK (6%), and Guyana (5%) (2023).
Imports - commodities
Key imports consist of refined petroleum, crude petroleum, cars, plastic products, and ships (2023).
Human Development Index
The country's Human Development Index (HDI) is 0.811, ranking it 69th out of 193 countries tested. (more information)